Week 7: Bonding and Shape
Week 6 | Week 7 (54% through semester) | Week 8
| Week 9 | Week 10 | Week 11Useful resources
Model 1: Lewis Structures
Lewis structures are used to model how the electrons are arranged in a covalent molecule. Dots represent electrons and a line between two atoms represents a bond that is formed by a pair of electrons.
Figure 1. Interactive Lewis Structure, developed by javalab.org
Worked example 1.
Draw the Lewis Structure of ethene (CH2CH2)
Step 1. Count the valence electrons from all the atoms – this can be
determined from the Periodic Table. For anions add and for cations
subtract the appropriate number of electrons
Carbon: 4 valence, Hydrogen: 1 valence
Step 2. Assemble the bonding framework. Decide which atoms are connected to each other and use a pair of electrons, represented by a line, to form a bond between each pair.
Carbon: 4 bonds, Hydrogen: 1 bond
Step 3. Arrange the remaining electrons as lone pairs and/or extra bonds so that each atom has 8 electrons (except H which has 2) including those within the bond.
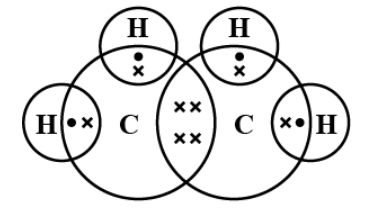
Step 4. Check for exceptions to the octet rule, and that all other atoms are satisfied. Add the overall charge, if needed. You are now complete!
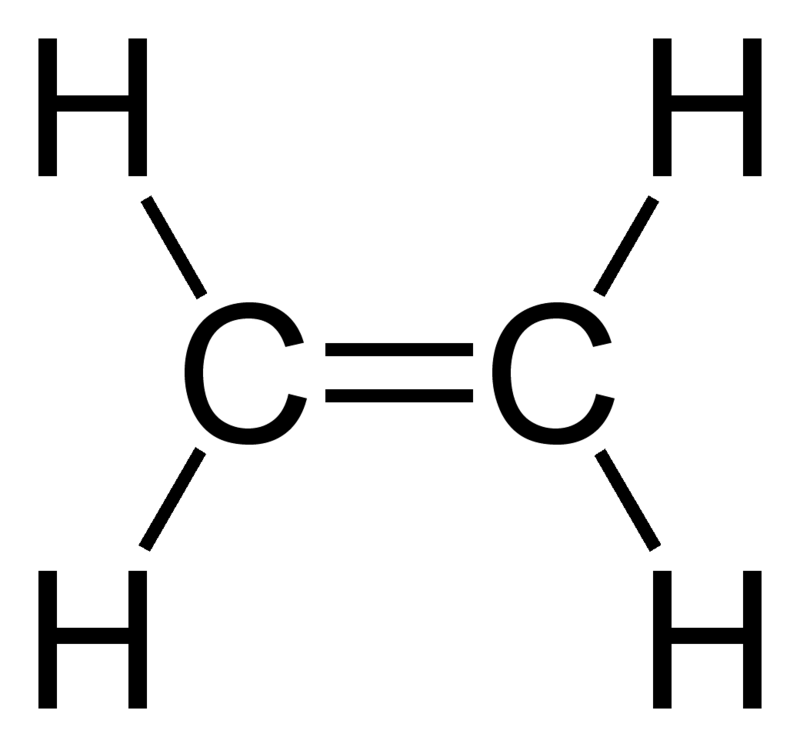
Worked example 2.
Draw the Lewis Structure of Iodine pentafluoride (IF5)
Always try to satisfy the octet rule first, then add lone pairs of electrons onto the least electronegative atom.
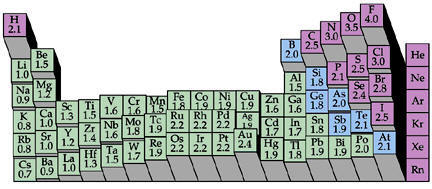
Figure 2. Diagram of electronegativity staircase
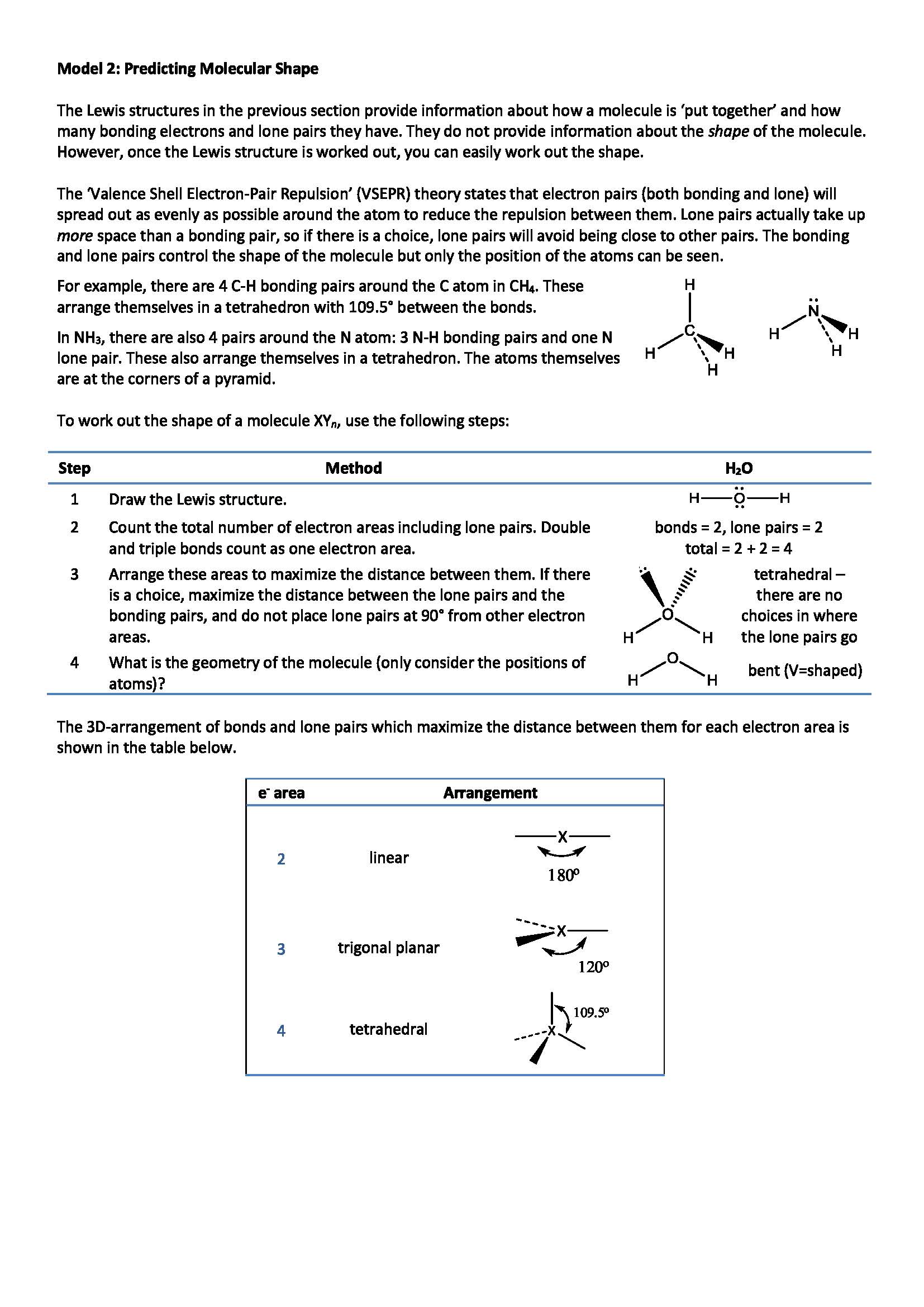
Model 2: Predicting Molecular Shape
Worked example 3.
Interactive 3D structure of ammonia (NH3)
Use the above 3D view of ammonia to draw out ammonia on the molecular shapes tool below.
Model 3: Bonding in Organic Molecules
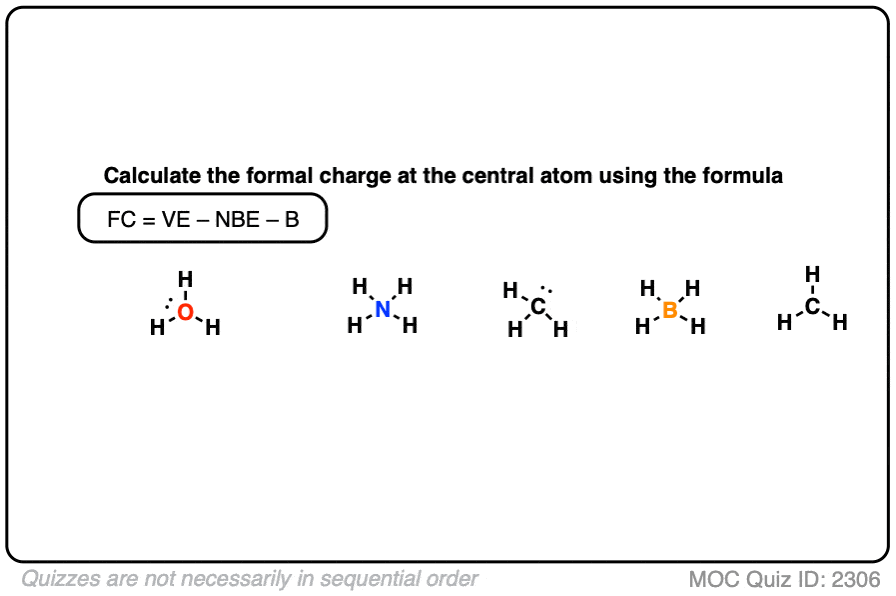
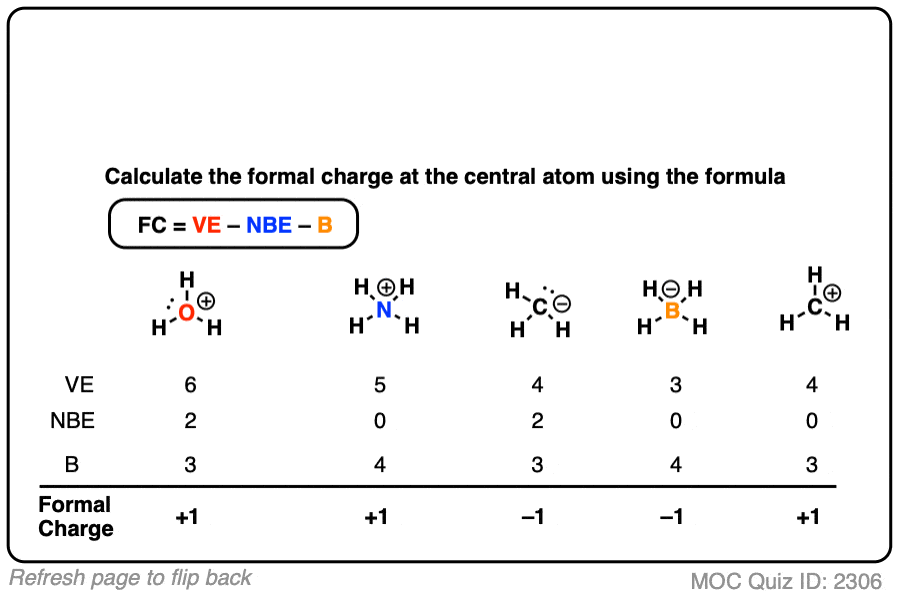
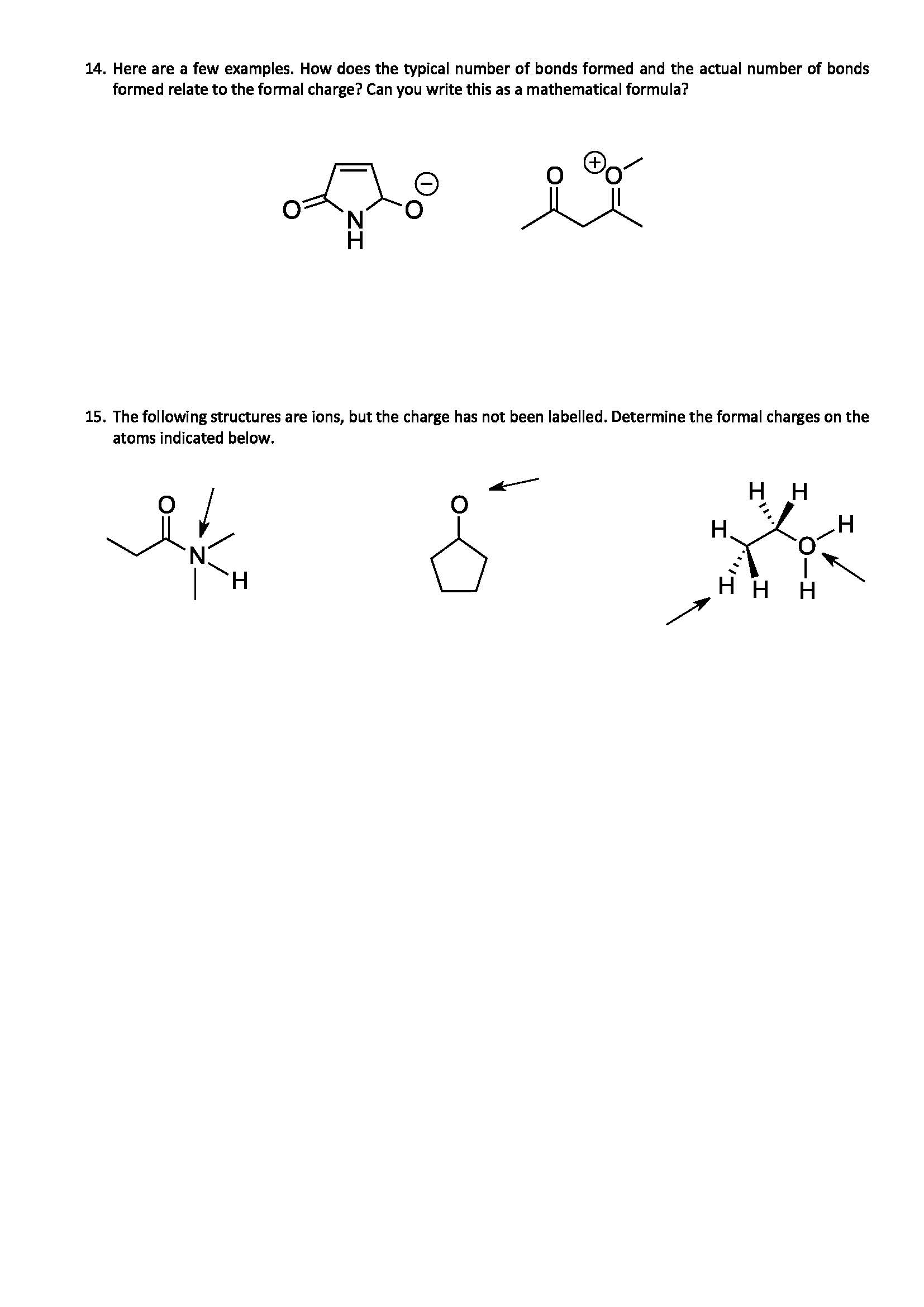
Textbook reading on Formal Charge (a bit advanced)
| = | formal charge | |
| = | number of valence electrons | |
| = | number of nonbonding valence electrons | |
| = | total number of electrons shared in bonds |
Worked example 4.